
After Hurricane Helene passed by, we had blue skies and wispy white clouds in the sky.

After Hurricane Helene passed by, we had blue skies and wispy white clouds in the sky.

It’s hard for me to believe that it’s only been 10 years since I started teaching at City Tech in Brooklyn. My gray hair seems like a testament to it being far longer.
I’ve been able to accomplish a lot of things since landing in Brooklyn as evidenced by my CV and Teaching Portfolio. I’ve had the joy of teaching great students, and I’ve enjoyed the collegiality and comradery of excellent coworkers.
Some of the greatest hits of things that I’ve done–some alongside the best colleagues and others by myself–include:
There’s a lot left to do. What can I accomplish in the next 10 years?

As I wrote at the beginning of July here, I planned to take advantage of LinkedIn Learning’s free one-month trial. I wanted to report back on my experience of taking LinkedIn Learning courses and provide more details about some of my tips that might help you be more successful with LinkedIn Learning.

I created the spreadsheet above in LibreOffice Calc as a list of all of the courses I had completed between June 29 and August 3 (I’m including the end of June courses in the free Career Essentials in Generative AI by Microsoft and LinkedIn that gave me the idea to continue with the free one month trial period). I included the instruction time for each course. This allowed me to calculate that I had completed 43 hours 11 minutes of course instruction across 39 courses during my LinkedIn Learning trial period.
I regret not keeping track of how long I spent on each course, which was far longer due to pausing the video to write notes, studying notes, taking quizzes, writing assignments, and taking exams. I believe the 50% extra time per course that I wrote about in July holds true.
I focused on two main areas: Generative AI, which I am building into my workflows and maintaining a pedagogical bibliography for here; and Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) Communication Best Practices, which I wanted to use to improve my teaching practices by structuring my classroom as supportive and welcoming to all students.
In the Generative AI courses, I learned about machine learning, different forms of generative AI, how generative AI is integrated (or being integrated) into local and server software, and frameworks for critique of AI systems in terms of ethics, bias, and legality. Also, I took some courses on Python to get an inkling of the code underpinning many AI initiatives today.
In the DEI Communication Best Practices cluster of courses, I learned helpful terminology, techniques for engagement, what to do to support and include others, and how to be an ally (mostly with an emphasis on the workplace, but thinking about how to leverage these lessons in the classroom). These courses covered combating discrimination, planning accessibility from the beginning and benefit of all, and supporting neurodivergence.
Overall, each learning experience was beneficial to my understanding of the topic. However, some instructors delivered better courses–for my way of learning–by employing repetition, anchoring key topics with words and definitions on the video (which you can pause and write down), giving more quizzes over shorter amounts of material (instead of fewer quizzes over longer time spans of material), and giving students mini projects or assignments to reinforce the lesson (e..g, pause and write about this, or pause the video, solve this problem, and “report back”–the course isn’t interactive but the “report back” idea is to compare your solution to the instructor’s after the video is played again).
All of the courses provide a lot of information in a very short amount of time. In some cases, the information compression is Latvian repack level. Even taking notes in shorthand, I could not keep up in some instances. To capture all of the information, I had to pause videos repeatedly, repeat (using the 10 second reply often) and read the transcript.
While I enjoyed the standalone courses, the Learning Paths provided a sequence and overlap in material that helped reinforce what was being taught. Also, Learning Paths helped me see connections between the broader implications of the topic (e.g., DEI, accessibility, neurodiversity, etc.) as well as explore certain aspects of the topic in more depth (e.g., how to approach conversations on uncomfortable topics or how to ask for permission to be an ally in a given situation).
Each instructor has a unique way of speaking and engaging the learner. I really enjoyed the diversity of the instructors across all topics.
The accessibility features built into LinkedIn Learning helped me follow along and make accurate notes. In particular, I always turned on closed captioning and clicked the “Transcript” tab beneath the video so that I could easily follow along and pause the video when there was a keyword or definition or illustration that I wanted to capture in my notes.

I added the course instruction time for those courses completed on the same day to generate the chart above that illustrates the ebb and flow of my course completion across the month. In some cases, I spread out the instruction across days to give myself enough time to learn and practice the topics being discussed (e.g., Python programming or Stable Diffusion image generation). There were other days that I paused my learning to work on my research or simply to take a break from learning.
On LinkedIn Learning, some of the courses are grouped together into what are called Learning Paths, which yield a separate certificate of completion from the certificates that you earn for each individual course. In some cases, as in the Career Essentials in Generative AI by Microsoft and LinkedIn also includes an exam with a time limit (1.5 hours) that must be passed before the Learning Path certificate is given. About 50% or 21 hours 45 minutes of the 43 hour 11 minute course instruction time applied to five earned Learning Paths for me:
Overall, I want to reiterate the tips that I wrote about here for being successful at LinkedIn Learning–both in terms of how you learn and how you demonstrate what you have learned. Below are some reiterated tips with details based on my experience this past month.

The one thing that I would like to stress above all others is how important it is to treat a LinkedIn Learning course like a classroom learning experience. What I mean by that is that you need to set aside quality time for learning, free from distraction, where you can take notes and complete the exercises, and study what you’ve learned before taking quizzes or exams. Employing your undivided attention, writing your notes by hand in a notebook, and completing quizzes, exams, and assignments all contribute to your learning, integrating what you’ve learned with your other knowledge, and preparing yourself to recall and apply what you’ve learned in other contexts, such as in a class or the workplace.
Unless you have eidetic memory, the fact is that you won’t learn a lot by passively watching or listening to courses. And even if you have photographic memory, all you will gain are facts and not the integration, connections, and recall that comes from using and reflecting on what you have learned.
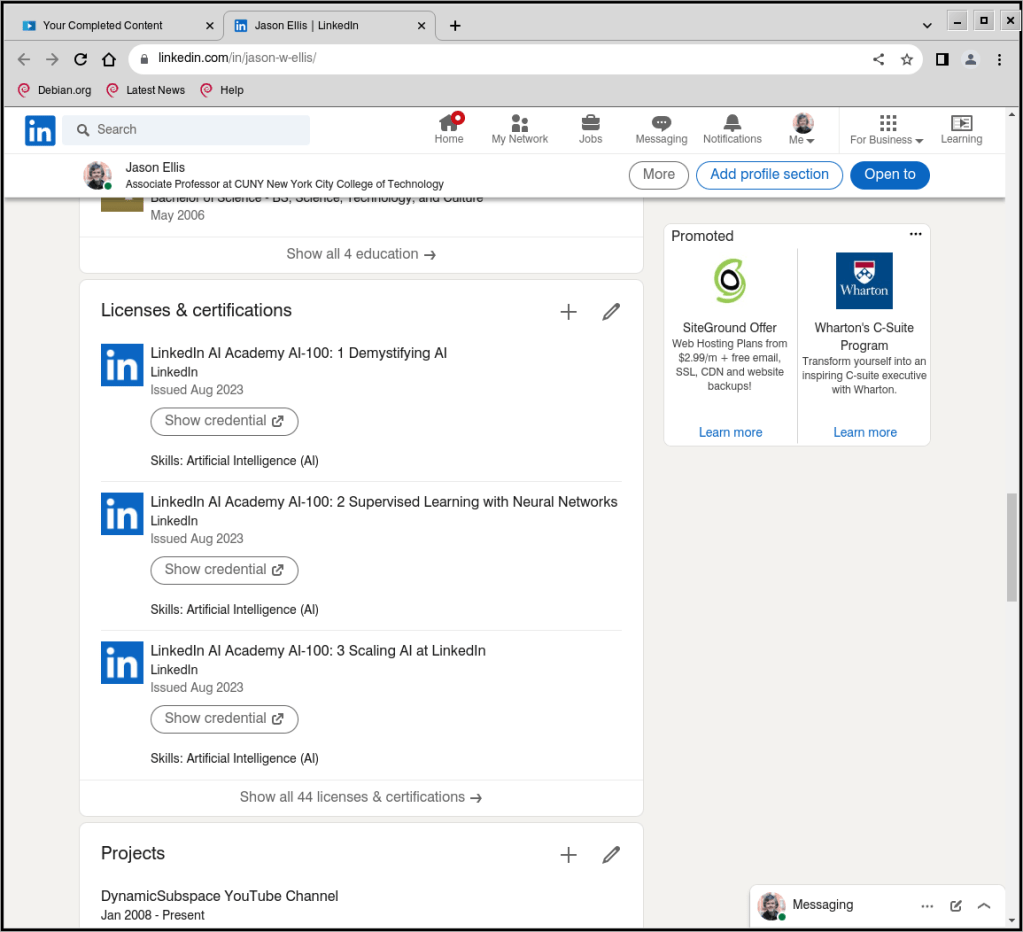
Remember to add each completed LinkedIn Course and Learning Path certification to your profile. They will appear in their own section as they do on mine shown above.
Completed Courses and Learning Paths do not automatically appear on your profile (consider: someone might not want all of their training to appear on their LinkedIn Profile for a variety of reasons).
To add a Course or Learning Path to your LinkedIn Profile, go to LinkedIn Learning > click “My Learning” in the upper right corner > click “Learning History” under “My Library” on the left > click the “. . .” to the right of the Course or Learning Path > click “Add to Profile” and follow the prompts.
LinkedIn also gives you the option to create post on your Profile about your accomplishment, which you should opt to do. When you do this, it auto suggests skills that it will add to your Skills section of your Profile. You can have up to 50 skills on your profile, so keep track of what’s there and prune/edit the list as needed to highlight your capabilities for the kinds of jobs that you are looking for. More on Skills further down the page.

As shown above and viewable on my CV here, I added links to my LinkedIn Course and Learning Path certifications in a dedicated section of my CV. In addition to the unique link to my certifications, I included the organization that issued it (i.e., LinkedIn), and the date of completion. You can do the same on your CV or resume.
To get the link to a Course or Learning Path completion certificate, go to LinkedIn Learning > click “My Learning” in the upper right corner > click “Learning History” under “My Library” on the left > click the “. . .” to the right of the Course or Learning Path > click “Download certificate” > click “LinkedIn Learning Certificate” > toggle “On” under the top section titled “Create certificate link” > Click “Copy” on the far right.
While you are here, you can download a PDF of your certificate for safe keeping at the bottom left of this last screen. You can add these PDFs to a professional portfolio or alongside a deliverable that you create based on the skills that you gained from that course to demonstrate your learning and mastery.
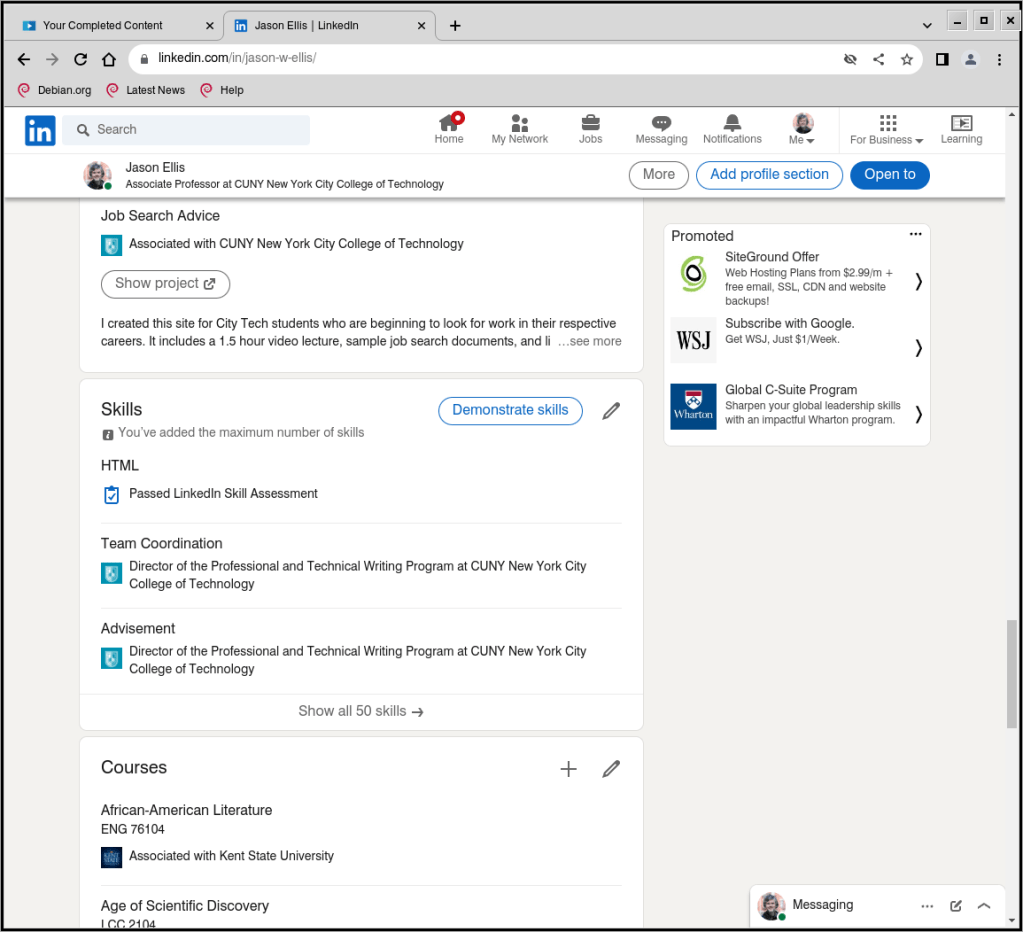
As I mentioned above, when you post about completing a course, LinkedIn Learning can autogenerate relevant skill terms to add to the Skills section on your Profile (as shown above on my Profile). When you have the spare time and focus, you should occasionally click on “Demonstrate skills” (you can do this without a LinkedIn Learning subscription). This gives you options for taking exams related to different skills that you’ve added to your Skills section of your Profile. If you pass, it provides some proof that you know something about that particular skill. Beware though: these exams can be tough. When I took the HTML exam, I discovered big gaps in what I knew from learning HTML years before without keeping up with changes to HTML in the intervening years. While I passed the exam, I made notes about those questions that I got wrong so that I knew what to learn more about to fill in those gaps.
Also, some skills don’t have exams associated with them. In those cases, you may submit a video or essay to demonstrate your experience to potential recruiters or hiring managers. If you do this, you should plan it out, shoot and edit your video to give the best visual and auditory impression, or write and revise your essay so that it is of the highest professional quality.
Looking back on what I learned, how I learned it, and who I learned it from, I’m glad that I invested the time and energy into a month of LinkedIn Learning. I’ve already started putting some of the lessons into practice (e.g., the generative AI and ethical AI courses), and I’m planning out how I will roll out the DEI approaches in my courses when I return to teaching in Fall 2024 (I am on sabbatical this academic year). In the future, I plan to pay for LinkedIn Learning when additional classes are available and I have the time to immerse myself in learning.
If you’re looking to skill up, I think that LinkedIn Learning can be beneficial if you go into it with a learning and reflective mindset. This means that you are willing to invest your attention, time, energy, and thought to learning the course material, want to reflect on how what you learn connects to other things you’ve already learned through school and work experience, apply what you’ve learned to deliverables that demonstrate you have integrated what you have learned (e.g., a detailed post on your LinkedIn Profile, a blog post, a poster, a video, an addition to your professional portfolio, etc.), and reflect, preferably in writing, on what you’ve learned, how you applied it, what you would like to see yourself accomplish next, and how to take those next steps.
As I said above, you likely won’t gain much by passively listening to LinkedIn Learning Courses while doing other things or being distracted by your environment. Invest in this form of learning and you will add to what you know and can do. In that spirit, it’s like my Grandpa Ellis used to tell me, “Jake, no one can take away your education!”
Hall, Donald E. The Academic Self: An Owner’s Manual. Columbus: Ohio State UP, 2002. Print.
I picked up Donald E. Hall’s The Academic Self from the Georgia Tech Library after completing my teaching assignment for Spring 2013–eleven years after the book had been published. Specifically, I was looking for books and articles to help me grapple with the challenges of this stage of my professional life as a postdoctoral fellow: teaching a 3-3 load, performing service duties, researching, writing, receiving rejections (and the far less often acceptance), and applying for permanent positions. In the following, I summarize Hall’s arguments, provide some commentary, and close with a contextualized recommendation.
Hall states in the introduction that the goal of The Academic Self is, “encourage its readership to engage critically their professional self-identities, processes, values, and definitions of success” (Hall xv). I found this book to be particularly useful for thinking through my professional self-identity. As I was taught by Brian Huot at Kent State University to be a reflective practitioner in my teaching and pedagogy, Hall argues for something akin to this in terms of Anthony Giddens’ “the reflexive construction of self-identity” (qtd. in Hall 3). Hall truncates this to be “self-reflexivity,” or the recognition that who we are is an unfolding and emergent project. I use this blog as part of my processes of self-reflection–thinking through my research and teaching while striving to improve both through conscious planning and effort.
However, unlike the past where the self was static and enforced by external forces, modernity (and postmodernity–a term Hall, like Giddens, disagrees with) has ushered in an era where the self is constructed by the individual reflectively. From his viewpoint, the self is a text that changes and can be changed by the individual with a greater deal of agency than perhaps possible in the past (he acknowledges his privileged position earlier in the book, but it bears repeating that this level of agency certainly is not equally distributed).
In the first chapter, titled “Self,” Hall writes, “Living in the late-modern age, in a social milieu already thoroughly pervaded by forms of self-reflexivity, and trained as critical readers, we academics in particular have the capacity and the professional skills to live with a critical (self-) consciousness, to reflect critically upon self-reflexivity, and to use always our professional talents to integrate our theories and our practices” (Hall 5). If we consider ourselves, the profession, and our institutions as texts to be read, we can apply our training to better understanding these texts and devise ways of making positive change to these texts.
He identifies what he sees as two extremes that “continue to plague academic existence: that of Casaubonic paralysis and Carlylean workaholism” (Hall 8). In the former, academics can be caught in a ignorant paranoia like Casaubon of George Eliot’s Middlemarch (1871-1872), or in the latter, academics can follow Thomas Carlyle’s call to work and avoid the “symptom” of “self-contemplation” (qtd. in Hall 6).
In the chapter titled “Profession,” Hall calls for us to apply our training to reflective analysis and problem solving of our professional selves and our relationship to the ever changing state of the profession itself. He questions to what extent the work of professionalism (seminars, workshops, etc.) are descriptive or prescriptive. “The ideal of intellectual work” varies from person to person, but it is an important choice that we each must make in defining who we are within the profession.
He reminds us that, “much of the pleasure of planning, processing, and time management lies not in their end products–publication or project completion–it is derived from the nourishment –intellectual, communal, and professional–provided by the processes themselves” (Hall 46). He builds his approach to process on his personal experiences: “Unlike some, I know well when my work day is over. Part of the textuality of process is its beginning, middle, and most importantly, its end” (Hall 46).
His talking points on process are perhaps the most practical advice that he provides in the book. In planning, he advises:
Hall goes on to suggest ten steps for professional invigoration to help folks suffering from a stalled career or burnout. However, these ten pieces of advice are equally applicable to graduate students, postdocs, and beginning faculty: join your field’s national organization, read widely in your field, set precise goals, maintain a daily writing schedule [my most difficult challenge], present conference papers, write shorter artifacts to support your research [reviews or my case, this blog], know the process and timeline of manuscript publishing, foster relationships with publishers and editors, politely disengage from poor or dysfunctional professional relationship/praise and value positive relationships, and find support in your local networks.
The final chapter, “Collegiality, Community, and Change,” reminds us, “always t put and keep our own house in order” (Hall 70). He suggests strategies counter to what he calls “the destructive ethos of ‘free agency’ that seems to pervade the academy today–the mindset that institutional affiliations are always only temporary and that individuals owe little to their departments or institutions beyond the very short term” (Hall 70). On professional attitudes, he encourages a focus on the local (institution) before national (beyond the institution), the current job as potentially your last job–treat it with that respect, meet institutional expectations, collegial respect of others, and learning the history of our institution/school/department from everyone with whom we work.
Perhaps most notably, he writes, “If we measure our success through the articulation and meeting of our own goals, as I suggest throughout this book, we can achieve them without begrudging others their own successes. However, if we need to succeed primarily in comparison to others, then we are deciding to enter a dynamic of competition that has numerous pernicious consequences, personal and inter-personal” (Hall 74-75). As I have written about on Dynamic Subspace before, it was the overwhelming in-your-faceness of others’ successes on social media like Facebook that distracted me from my own work. Seeing so many diverse projects, publications, and other accomplishments made me question my own works-in-progress before they had time to properly incubate and grow. For all of social media’s useful and positive aspects for maintaining and growing networks of interpersonal relationships, I had the most trouble resisting the self-doubt that the Facebook News Feed generated for me.
Finally, he encourages dynamic and invested change in departments and institutions. However, as junior faculty, it is important to research and weigh the possible repercussions for working to make change. Hall is not arguing against change by those without tenure, but he is warning us to proceed cautiously and knowledgeably due to a number factors: potential sources of resistance, jeopardizing our jobs, etc.
Hall’s “Postscript” reinforces the overarching idea of ownership by calling on the reader to live with “intensity,” an idea that inspired Hall from Walter Pater’s 1868 The Renaissance: “burn always with [a] hard, gem-like flame” (qtd. in Hall 89). Hall’s intensity is one self-motivated, well-planned, dynamically agile, and passionately executed.
Hall’s The Academic Self is a very short read that is well worth the brief time that it will take to read. It offers some solid advice woven with the same theoretically infused self-reflexivity that he encourages. It practices what it preaches. The main thing to remember is that the book is eleven years old. When it was published, the field of English studies was experiencing an employment downturn (albeit one not as pronounced as in recent years). Michael Berube’s “Presidential Address 2013–How We Got Here” (PMLA 128.3 May 2013: 530-541), among many other places–this issue just arrived in the mail today, so I was reading it between chapters of Hall’s book, picks up some of the other challenges that graduate students, postdoctoral fellows, and junior faculty have to contend with in the larger spheres of the profession and society. The other advice that Hall provides on personal ownership and collegiality, I believe, remains useful and inspirational. In addition to reading Hall’s book, you should check out his bibliography for further important reading in this vein.
2012 was a big year for me. I earned my PhD and I obtained my first job with that degree. I traveled for my research–first to California, then to Detroit, and later to Germany. And, my wife, our cat, and I relocated from Ohio to Atlanta for my new job at Georgia Tech and we moved into my old house in Norcross, which had not sold during the past six years of graduate school.
Unlike years past, I thought that it might be appropriate to jot down some of the milestones of 2012. Here are a few of those big things: